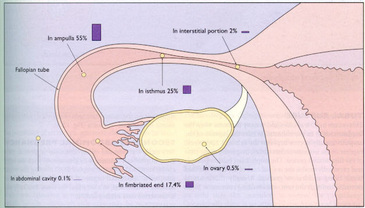
Ninety-five percent of ectopic pregnancies occur in the fallopian tube, but there are some ectopic pregnancies that occur in other places. These include:
1. Cornual/interstitial ectopic pregnancy
2. Ovarian ectopic pregnancy
3. Abdominal ectopic pregnancy
4. Caesarean scar pregnancy
5. Cervical ectopic pregnancy
These so called non-tubal ectopic pregnancies tend to present differently than tubal pregnancies and because of their atypical presentation are potentially more dangerous in fact, the majority of fatalities in the last Triennium in the United Kingdom were due to these sort of pregnancies.
1. Cornual/interstitial ectopic ectopic pregnancy.
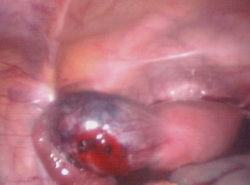
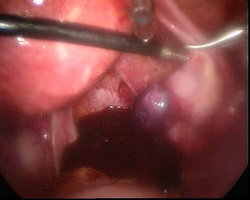
These are pregnancies that are located at the junction of the fallopian tube and the uterus. This is the most muscular part of the uterus. They occur in about 1:2500-5000 live births and are responsible for about 2-4% of ectopic pregnancies. In the last triennium in the UK they were responsible for about 40% of deaths from ectopic pregnancy. Patients with this type of pregnancy have a 7 times chance of dying from it than women with tubal pregnancies. They are dangerous because women tend to present later in pregnancy than with tubal ectopic pregnancies and tend to present when the pregnancy has ruptured and internal bleeding has occurred.
2. Ovarian ectopic pregnancy
This is where the pregnancy rather than implanting in the uterus implants in the ovary. Their incidence is about 1:3000-7000 pregnancies and 0.1-3% of ectopic pregnancies. These pregnancies tend to present after internal bleeding has occurred. They also tend to occur in women who have had children and who have intrauterine contraceptive device for contraception
3. Abdominal pregnancy
This is where the pregnancy implants outside the uterus away from the female reproductive organs. They can be very difficult to diagnose and sometimes the babies survive till very late in pregnancy though very few survive. These pregnancies can be responsible for profuse internal bleeding.
4. Caesarean scar pregnancy
This is a more modern phenomenon and has been on the increase with the increasing number of caesareans performed in modern society. It occurs in women who have had a previous caesarean section. It can sometimes be very difficult to diagnose
5. Cervical pregnancy
Technically these pregnancies are in the uterus but very low down. The structure of the uterus is different from that of the cervix. When pregnancies implant in the cervix there is less room for expansion and the pregnancies rarely survive.






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed