Laparoscopic myomectomy with the use of these techniques may also be very appropriate for Jehovah’s witnesses who want to undergo myomectomy.
The Key to surgery is optimization of the patient before surgery. So if blood count is low iron therapy is recommended.
If heavy periods are a problem and it is difficult to bring iron levels up, your doctor may advise that you use hormones to temporarily stop your periods. The most commonly used are GnrH analogues.
GnRH analogues are substances that shut the ovaries down, “tricking” the body into thinking that it is going through the change. It can be given for up to 3 months and shrinks the fibroids by about 30%.
Some doctors prefer not to use these substances, as there are reports in medical literature that it may make the plane of cleavage of the fibroid more difficult to identify.
It can thus be responsible for either making the operation more difficult thus increasing blood loss rather than preventing it.
A more recent drug called ESMYA Ulipristal acetate (a progesterone receptor antagonist) has recently been approved for the pre-operative management of uterine fibroids. As it is new there are no studies on surgical outcomes yet. But it may have the advantage of fewer side effects than GnRH analogues.
Other substances can be used intra-operatively to prevent blood loss during myomectomy
Misoprostol: this drug is commonly used to prevent post partum hemorrhage and has been shown to effectively reduce blood loss during removal of fibroids.
Vasopressin: this drug is a powerful vasoconstrictor and prevents blood loss during removal of fibroids because it is so powerful it is diluted.
It is not available in all countries.
Bupivacaine and adrenaline; has the same effect as vasopressin but is weaker
Physical tourniquets that temporarily occlude major blood vessels supplying the womb can also be used during surgery both at open and laparoscopic surgery
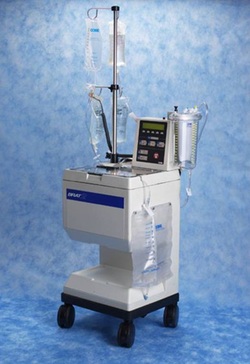
Cell-savers are mechanical devices that process blood from the site of operation of the patient and is recycled once processed and analysed. It is more useful at open surgery than at laparoscopy.
It is important that women discuss these issues with their doctors so they know which of these methods would be used to prevent blood loss in their individual case.
Remembering that less blood loss sometimes also equals less adhesion formation.






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed